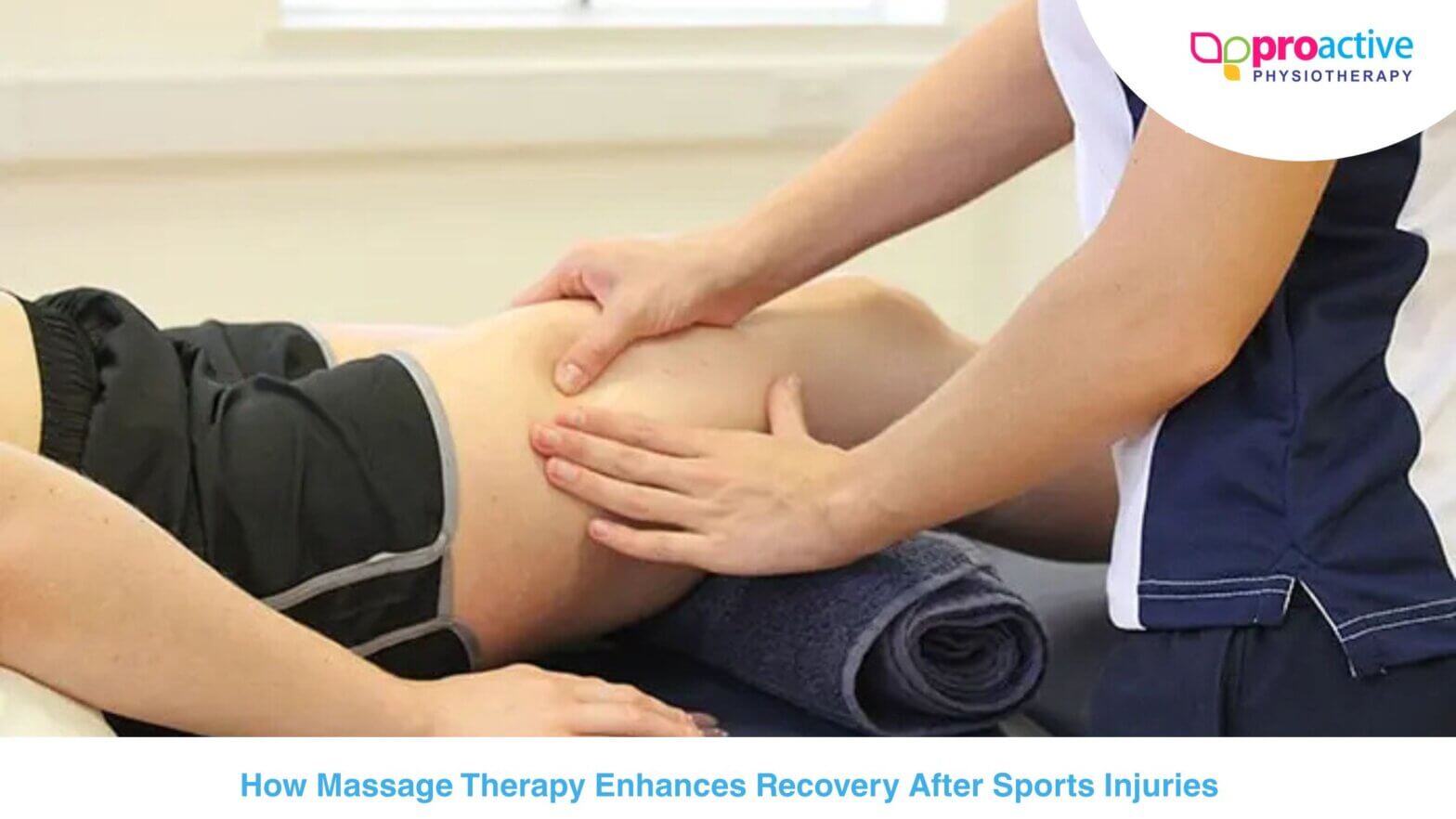
As an exercise science professional, it’s important to not only understand how to prevent musculoskeletal injuries but also how to properly rehab them. Whether your client has suffered from a sprained ankle, rotator cuff tear, or even lower back pain, rehabilitation techniques must be tailored to their individual needs.
One of the most critical steps in the rehab process is restoring proper joint mobility and range of motion. This can be achieved through manual therapy techniques such as stretching and massage, as well as exercises that target the injured area specifically.
Strengthening exercises are also crucial in rehabilitation. Progressive overload should be applied gradually to help rebuild strength without causing further injury. This can include bodyweight exercises, resistance band exercises or weightlifting.
In many cases, proprioception (the sense of knowing one’s body position in space) may have been compromised due to injury or surgery. Incorporating balance and coordination drills into rehab programs can help restore this vital skill set.
Overall, successful rehabilitation requires an individualized approach that addresses each client’s unique needs and goals. With a well-rounded program that emphasizes joint mobility, strength training and proprioception work, clients can make a full recovery from musculoskeletal injuries with confidence.
Strengthening exercises for ACL injuries
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries are a common occurrence in the world of exercise science, and they require proper rehabilitation techniques to ensure quick recovery. One effective approach is strengthening exercises, which can help you regain stability and balance while reducing the risk of future damage.
The focus of these exercises should be on improving quadriceps and hamstring strength, as these muscles work together to support the knee joint. Examples of strengthening exercises for ACL injuries include lunges, squats, leg presses, and leg extensions. Resistance can also be added through the use of weights or resistance bands.
It’s important to remember that proper form is key when performing these exercises. Ensure that your knees are in alignment with your toes, your back is straight, and your core is engaged to avoid causing further injury or strain to surrounding muscles.
While strengthening exercises are an integral part of rehabilitating ACL injuries, it’s important to consult with a certified medical professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise routine. They can help tailor a program based on your specific injury and abilities while monitoring progress and ensuring safety throughout the rehabilitation process.
Taping methods for rotator cuff injuries
Rotator cuff injuries are one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries in exercise science. They can cause pain and discomfort, limit range of motion and affect overall athletic performance. Tape is a popular and effective way to manage rotator cuff injuries by providing support and stability to the affected area.
There are two main taping methods for rotator cuff injuries:
1. Kinesiology tape: This is a stretchy, adhesive tape that mimics the elasticity and strength of human skin. Kinesiology tape is applied directly over the injured area in a specific pattern designed to provide support to the rotator cuff muscles.
2. Athletic tape: This is a non-elastic adhesive tape that is used to support joints and muscles during physical activity. Athletic tape can be used to restrict movement in the shoulder joint, reducing stress on the rotator cuff muscles.
Both taping methods can be beneficial for managing rotator cuff injuries but it’s important to use them correctly for optimal results. Consider seeking guidance from a certified sports medicine professional before attempting any taping technique on your own.
In summary, taping methods can provide support and stability to the affected area in order to manage rotator cuff injuries effectively. If you have this type of injury, accessing support from sports medicine professionals must be prioritized before proceeding with any self-treatment plan, recovery program or rehabilitation process.
Stretching techniques for plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often frustrating injury that can occur in athletes and individuals who are physically active. This condition typically presents as pain and tightness in the bottom of the foot near the heel, making it difficult to walk or run without discomfort. Fortunately, there are a variety of stretching techniques that can help alleviate plantar fasciitis symptoms.
One effective technique involves rolling a tennis ball or golf ball under the foot for several minutes at a time. This helps to massage and loosen up the plantar fascia, which can become tight and inflamed with excessive activity. Another useful stretch involves standing on a step with the balls of the feet on the step edge, then lowering the heels downward to feel a stretch through the arch and calf muscles.
It’s important to note that stretching alone may not be enough to fully treat plantar fasciitis. Other interventions such as strengthening exercises, ice therapy, and modifying activity levels may also be necessary for optimal recovery. Consulting with a physical therapist or sports medicine professional can help athletes develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to their specific needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, proper rehabilitation techniques are essential for effectively treating common musculoskeletal injuries in exercise science. Strengthening exercises for ACL injuries can help improve stability and prevent future injury, while taping methods for rotator cuff injuries can provide support during activity. Stretching techniques for plantar fasciitis can help reduce pain and improve flexibility. However, it is important to remember that each injury is unique and requires a personalized approach to rehabilitation. Consistent efforts towards proper recovery can ensure successful outcomes and allow individuals to return to their active lifestyles with confidence.
FAQ
Can I perform strengthening exercises for an ACL injury without consulting a medical professional?
No, it is important to consult with a certified medical professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise routine to ensure safety and tailor the program based on your specific injury and abilities.
Are there any risks associated with using tape for managing rotator cuff injuries?
Yes, improper use of tape can lead to skin irritation or even make the injury worse. It’s important to seek guidance from a certified sports medicine professional before attempting any taping technique on your own.
Can stretching techniques alone fully treat plantar fasciitis?
No, while stretching can help alleviate symptoms, other interventions such as strengthening exercises, ice therapy, and modifying activity levels may also be necessary for optimal recovery. Consulting with a physical therapist or sports medicine professional can help athletes develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to their specific needs.
What is proprioception and why is it important in rehabilitation?
Proprioception is the sense of knowing one’s body position in space. It is important in rehabilitation because many injuries or surgeries can compromise this skill set. Incorporating balance and coordination drills into rehab programs can help restore proprioception.
Why is restoring joint mobility and range of motion crucial in rehabilitation?
Restoring joint mobility and range of motion is crucial in rehabilitation because it helps prevent stiffness which could limit functional movement. This can be achieved through manual therapy techniques such as stretching and massage, as well as exercises that target the injured area specifically.